Learn about the symptoms of magnesium deficiency, such as tetany and tight muscles. Discover how to combat this issue with diet and supplements.
Introduction
Did you know that magnesium deficiency is more common than you might think? Up to 88% of people are low in this essential mineral, which can lead to symptoms like tetany, tight muscles, insomnia, anxiety, fatigue, migraines, and kidney stones. It can be challenging to test for magnesium deficiency, as only 1% of magnesium is found in the blood, so increasing your intake of magnesium-rich foods and supplementing with magnesium glycinate can help combat this issue.
To reverse a magnesium deficiency, it’s vital to understand the symptoms and causes, such as diet, gut inflammation, diabetes, excessive sugar consumption, and certain medications. Increasing your magnesium intake through foods like sea kelp, almonds, nutritional yeast, and leafy greens, as well as supplementing with 800mg of magnesium glycinate, can improve your magnesium levels over time.
While chronic magnesium deficiency may take up to a year to fix, many individuals experience an improvement in their symptoms within weeks or months, ultimately leading to better overall health and well-being.
Overview of Magnesium Deficiency
Magnesium deficiency is a common issue, with up to 88% of people being low in this essential mineral. However, testing for magnesium deficiency can be challenging since only 1% of magnesium is found in the blood. Factors contributing to magnesium deficiency include dietary choices, gut inflammation, diabetes, excessive sugar consumption, and certain medications.
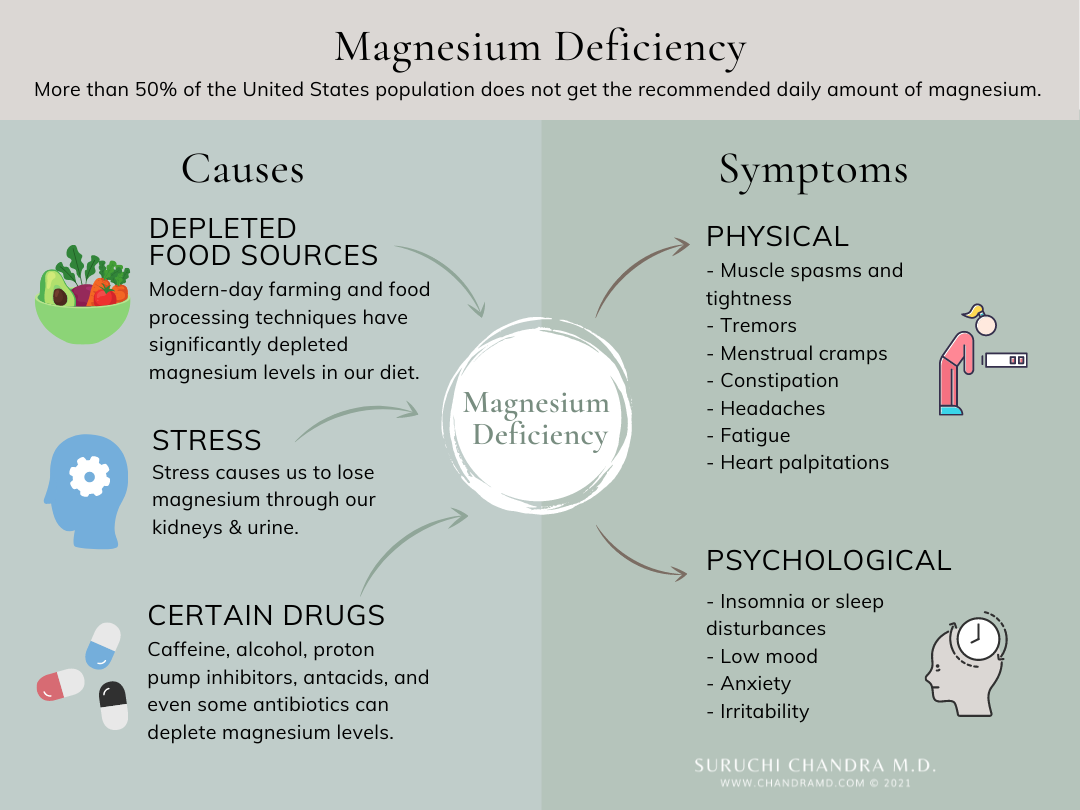
Causes of Magnesium Deficiency
Dietary factors
Your magnesium levels can be influenced by your diet. Consuming foods low in magnesium or having poor absorption of magnesium-rich foods can lead to deficiency.
Gut inflammation
Inflammation in the gut can impair the absorption of magnesium from the foods you eat, contributing to a deficiency over time.
Diabetes
Individuals with diabetes may have an increased risk of magnesium deficiency due to altered metabolism and excretion of magnesium in the body.
Excessive sugar consumption
High sugar intake can impact magnesium levels by promoting urinary excretion and impairing magnesium absorption in the gut.
Certain medications
Some medications, such as antibiotics, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), antacids, and diuretics, can interfere with magnesium absorption or increase excretion, leading to a deficiency.

This image is property of i.ytimg.com.
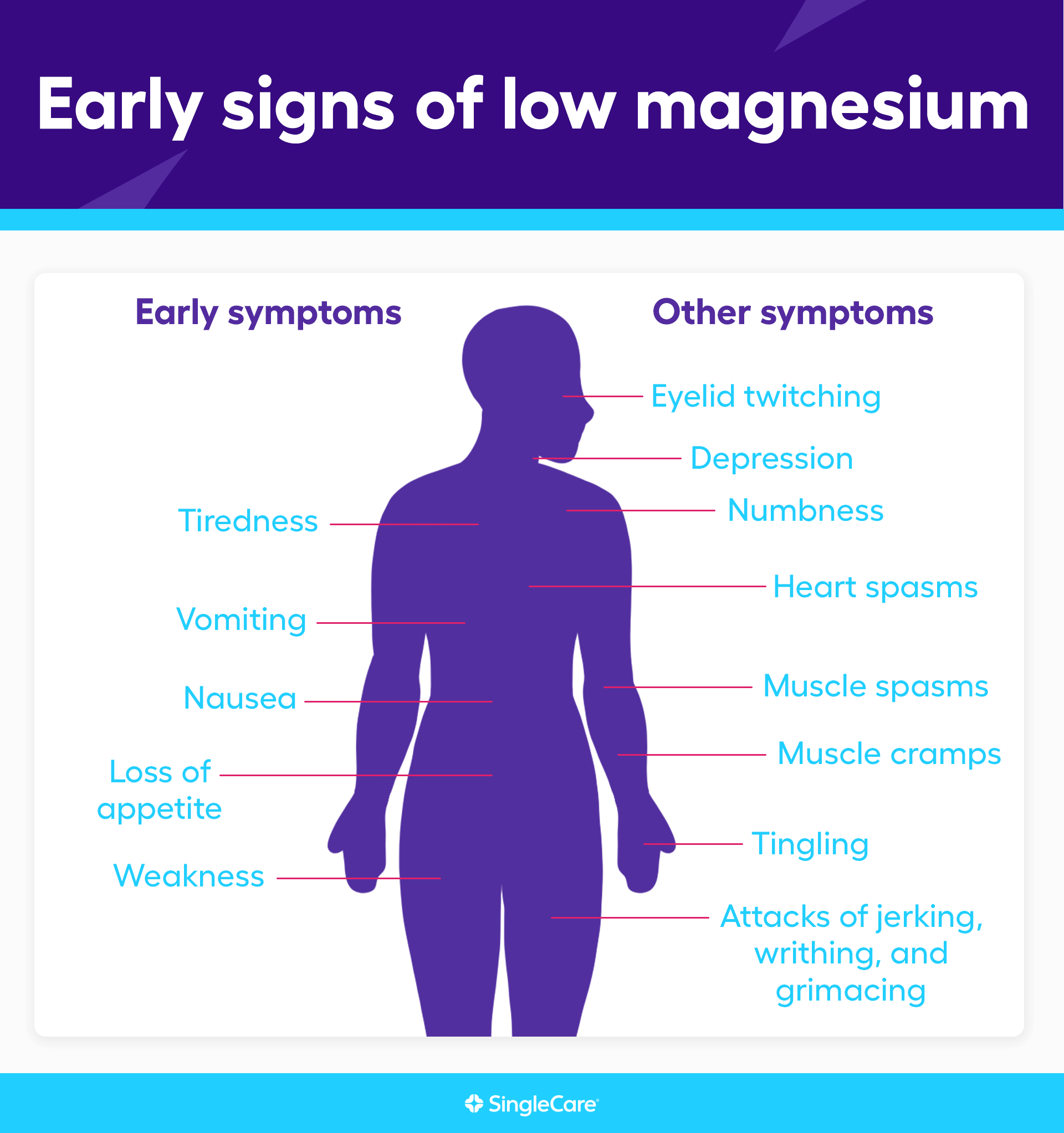
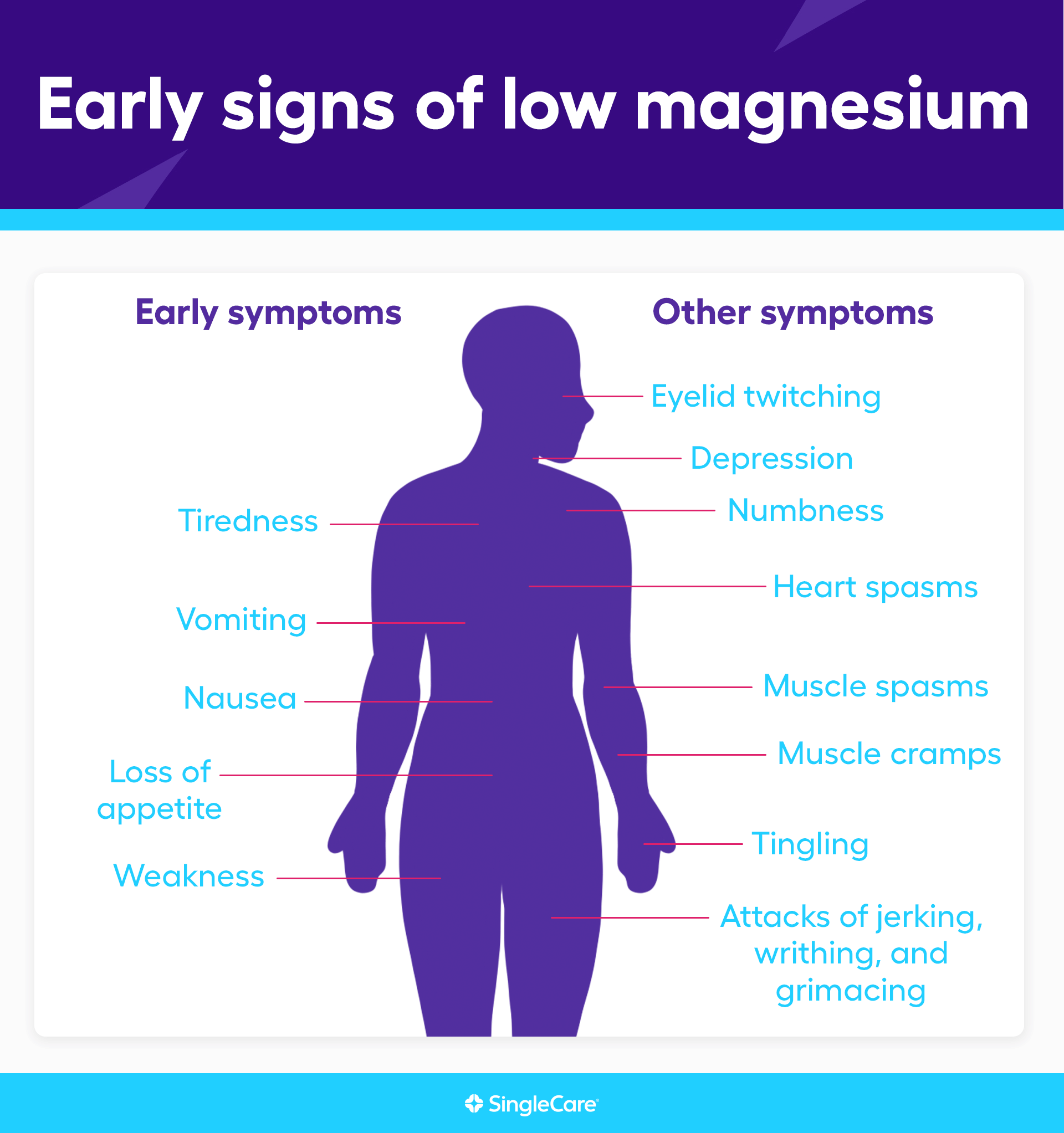
Symptoms of Magnesium Deficiency
Tetany
Low levels of magnesium can cause muscle spasms, twitches, or cramps known as tetany.
Tight muscles
Muscle tightness or stiffness can be a symptom of magnesium deficiency, as magnesium plays a crucial role in muscle relaxation.
Insomnia
Magnesium deficiency may contribute to sleep disturbances, including difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep.
Anxiety
Low magnesium levels can affect neurotransmitter function, potentially leading to symptoms of anxiety or heightened stress.
Fatigue
Magnesium is essential for energy production in the body. Deficiency can result in feelings of fatigue or low energy levels.
Migraines
Individuals with magnesium deficiency may experience more frequent or severe migraines due to magnesium’s role in neurotransmitter regulation.
Kidney stones
Magnesium deficiency can contribute to the formation of kidney stones, as magnesium helps prevent the accumulation of calcium in the kidneys.
Foods High in Magnesium
Sea kelp
Sea kelp is a rich source of magnesium, providing 760mg per 100 grams.
Almonds
Almonds are a nutrient-dense snack that offers 490mg of magnesium per 100 grams.
Nutritional yeast
Nutritional yeast is a vegan-friendly option high in magnesium, with 231mg per 100 grams.
Pecans
Pecans are a tasty nut that contains 142mg of magnesium per 100 grams.
Leafy greens
Leafy greens like spinach and kale are packed with magnesium, offering around 100mg per 100 grams.
Dark chocolate
Dark chocolate is not only delicious but also a good source of magnesium, providing 165mg per 100 grams.
Pumpkin seeds
Pumpkin seeds are a convenient snack packed with 265mg of magnesium per 100 grams.
Meat
Meat, such as beef or chicken, contains smaller amounts of magnesium, ranging from 25 to 35mg per 100 grams.
Fish
Fish like salmon or mackerel also contain magnesium, with similar amounts to meat at around 25 to 35mg per 100 grams.

This image is property of d16qt3wv6xm098.cloudfront.net.
Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) of Magnesium
The recommended daily intake of magnesium ranges from 300 to 420mg. However, studies indicate that the average person only consumes about 215 mg of magnesium daily.
Strategies to Combat Magnesium Deficiency
Increase intake of magnesium-rich foods
Boosting your consumption of magnesium-rich foods can help replenish and maintain adequate levels of magnesium in your body.
Supplementation with 800 mg of magnesium glycinate
Taking a magnesium glycinate supplement at a dosage of 800 mg daily can support your magnesium levels, especially if you have a deficiency.
Maintenance of the diet after supplementation
After addressing a magnesium deficiency with supplementation, it’s crucial to continue consuming magnesium-rich foods to maintain optimal levels in the long term.
This image is property of images.ctfassets.net.
Reversing Chronic Magnesium Deficiency
Chronic magnesium deficiency may take up to a year to fully rectify, but improvements in symptoms can be experienced within weeks or months. It is essential to follow a consistent approach to replenishing magnesium levels to ensure long-term health benefits.
Timeline for improvement
The timeline for improvement in magnesium deficiency symptoms may vary among individuals, with some experiencing relief sooner than others. Consistent supplementation and dietary changes are key to reversing chronic deficiency.
Dr. Eric Berg DC’s recommendations
Dr. Eric Berg DC suggests supplementing with magnesium glycinate at a dose of 800mg daily to combat magnesium deficiency. Following supplementation, maintaining adequate magnesium levels with a balanced diet is crucial for long-term health.
Conclusion
Recognizing and addressing magnesium deficiency is vital for overall health. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and strategies to combat magnesium deficiency, individuals can take proactive steps to improve their well-being.
Whether through dietary changes, supplementation, or long-term maintenance, managing magnesium levels can contribute to alleviating symptoms and enhancing overall health and vitality. Remember, prioritizing your magnesium intake can make a significant difference in how you feel and function on a daily basis.
This image is property of images.squarespace-cdn.com.